Rules of Origin Facilitator: a new tool to help MSMEs benefit from tariff preferences
16 October 2018
There are currently over 400 free trade agreements and preferential trade arrangements in place worldwide, which establish lower rates of Customs duties for certain goods provided that specified origin criteria are met. However, many companies ignore the fact that they can claim tariff preferences, or, if they do know that such schemes exist, they do not understand how to verify that the goods they buy or sell are eligible for preferential treatment.
As a result, many potential beneficiaries pay the tariff that applies to goods originating in countries that are not part of the agreement, losing the comparative advantage vis-à-vis their competitors, with many exporters losing business opportunities too. Micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) are especially impacted. According to a survey on non-tariff measures undertaken by the International Trade Centre (ITC) in over 60 countries, rules of origin and related certification requirements are among the most frequently cited trade obstacles by this category of companies.
About the tool
To make it easy for traders to navigate the complex landscape of trade agreements, the ITC and the WCO have developed an online tool called the “Rules of Origin Facilitator” (findrulesoforigin.org), which acts as a gateway to such agreements. The tool enables users to determine whether a specific product is covered by a preferential scheme and find the rules of origin that must be complied with in relation to a particular scheme.
Besides product-specific rules of origin, the tool also highlights provisions on origin certification, cumulation, the audit trail, shipment and invoicing, in addition to indicating which documentation is required (for example, a certificate of origin), and where to find information on national authorities’ websites.
It currently covers more than 70 trade agreements applied by 85 countries as well as the non-preferential regimes of the European Union, the United States and Switzerland. The ITC is continuously increasing the tool’s coverage – the objective being that it will eventually encompass all existing trade agreements.
Using the tool
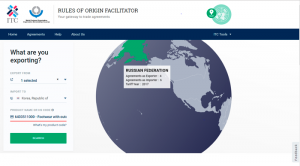
The tool’s homepage shows a search engine. Users must select a country, or several countries, of export and a country of import, and then search using the Harmonized System (HS) Customs classification code of the product of interest. If the user does not know the HS code of the product he wishes to sell or buy, he can enter the product name (shoes, for example) and the tool will display several classification possibilities. A link to the “product nomenclatures” search engine maintained on the ITC’s Market Access Map also shows on the homepage.
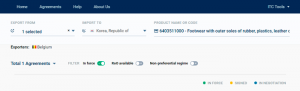
The result page shows all available trade agreements corresponding to the selected parameters. The tool allows filtering between agreements already in force and those that are still to be implemented. It also allows the filtering out of agreements where detailed rules of origin are not yet available (i.e. agreements already in force but not yet covered by the tool).
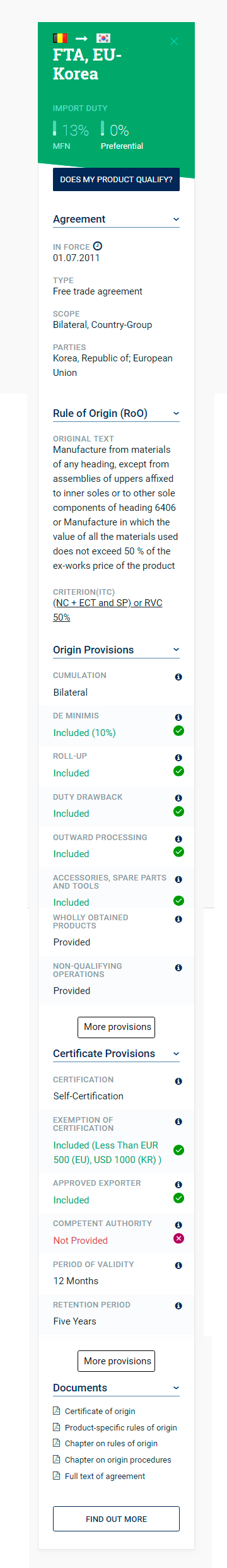
When a trade agreement or a preferential trade arrangement exists between selected countries, the tool shows basic information, such as the difference between the preferential and the most favoured nation (MFN) duty rates as well as other information, such as the date of entry into force of the scheme and the parties involved.
Users can access further details on the agreements covered by the tool, including the exact wording of the rules of origin, the cumulation provisions and possible shipment requirements as well as information related to the origin certificate, such as the details of the issuing authority and the validity period.
As several exporting countries can be selected, the tool allows requirements across agreements to be compared. Information icons also appear next to each category of provisions, providing users with a definition of the terms used as well as examples of how they can be applied.
Multiple benefits
With this new tool, the WCO and the ITC hope to improve the transparency of trade rules and to facilitate the work of MSMEs. Ultimately, the tool is expected to contribute to a reduction in trade obstacles associated with rules of origin, and increasing utilization of preferences under trade agreements.
The tool is very easy to use. Try it and let us know what you think by using the tool’s feedback function.
